 IIA TANMOY SAMANTA
IIA TANMOY SAMANTAUnveiling the Dynamics and Genesis of Small-scale Fine-structure Loops in the Lower Solar Atmosphere
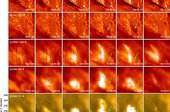
Recent high-resolution solar observations have unveiled the presence of small-scale loop-like structures in the lower solar atmosphere, often referred to as unresolved fine structures, low-lying loops, and miniature hot loops. These structures undergo rapid changes within minutes, and their formation mechanism has remained elusive. In this study, we conducted a comprehensive analysis of two small loops utilizing data from the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph (IRIS), the Goode Solar Telescope (GST) at Big Bear Solar Observatory, and the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly and the Helioseismic Magnetic Imager on board the Solar Dynamics Observatory, aiming to elucidate the underlying process behind their formation. The GST observations revealed that these loops, with lengths of ∼3.5 Mm and heights of ∼1 Mm, manifest as bright emission structures in Hα wing images, particularly prominent in the red wing. IRIS observations showcased these loops in 1330 Å slit-jaw images, with transition region (TR) and chromospheric line spectra exhibiting significant enhancement and broadening above the loops, indicative of plasmoid-mediated reconnection during their formation. Additionally, we observed upward-erupting jets above these loops across various passbands. Furthermore, differential emission measurement analysis reveals an enhanced emission measure at the location of these loops, suggesting the presence of plasma exceeding 1 MK. Based on our observations, we propose that these loops and associated jets align with the minifilament eruption model. Our findings suggest a unified mechanism governing the formation of small-scale loops and jets akin to larger-scale X-ray jets.
 IIA ARKAPRABHA SARANGI
IIA ARKAPRABHA SARANGIA Multiwavelength Autopsy of the Interacting Type IIn Supernova 2020ywx: Tracing Its Progenitor Mass-loss History for 100 Yr Before Death
While the subclass of interacting supernovae (SNe) with narrow hydrogen emission lines (Type IIn supernovae (SNe IIn)) consists of some of the longest-lasting and brightest supernovae (SNe) ever discovered, their progenitors are still not well understood. Investigating SNe IIn as they emit across the electromagnetic spectrum is the most robust way to understand the progenitor evolution before the explosion. This work presents X-ray, optical, infrared, and radio observations of the strongly interacting Type IIn supernova, SN 2020ywx, covering a period >1200 days after discovery. Through multiwavelength modeling, we find that the progenitor of 2020ywx was losing mass at ∼10−2–10−3 M⊙ yr−1 for at least 100 yr pre-explosion using the circumstellar medium (CSM) speed of 120 km s−1 measured from optical and near-infrared (NIR) spectra. Despite the similar magnitude of mass loss measured in different wavelength ranges, we find discrepancies between the X-ray and optical/radio-derived mass-loss evolution, which suggest asymmetries in the CSM. Furthermore, we find evidence for dust formation due to the combination of a growing blueshift in optical emission lines and NIR continuum emission which we fit with blackbodies at ∼1000 K. Based on the observed elevated mass loss over more than 100 yr and the configuration of the CSM inferred from the multiwavelength observations, we invoke binary interaction as the most plausible mechanism to explain the overall mass-loss evolution. SN 2020ywx is thus a case that may support the growing observational consensus that SNe IIn mass loss is explained by binary interaction.
 IIA MUTHU PRIYAL, V
IIA MUTHU PRIYAL, VObservations of Temporal Variations in the 5303 Å Emission Line During a Coronal Mass Ejection Without Any Associated Solar Flare
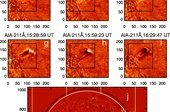
Reports using total solar eclipse data indicate that the 5303 Å emission line is a promising tool for observing the thermodynamic changes due to coronal mass ejections (CMEs) close to the Sun. The Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC) on board ADITYA-L1, the recently launched first Indian space solar mission, has now provided an opportunity to regularly observe the solar corona in the 5303 Å emission line. We present the first long-duration temporal observations of activity associated with a flareless CME from an active region at the west limb of the Sun, with the VELC. The observations were in the sit-and-stare mode for ≈7 hr. Our analysis shows a steady increase in the intensity of the line by ≈57%, followed by a gradual decrease to the initial level. The width of the line also showed changes, but opposite to that in the intensity. The width slowly decreased from 0.97 ± 0.01 Å to 0.87 ± 0.01 Å and then increased back. The change is ≈10%. The effective temperatures corresponding to each of the above two widths are 3.39 ± 0.1 × 106 K and 2.74 ± 0.1 × 106 K, respectively. The Doppler velocity changed gradually from 0 ± 0.5 km s−1 to −3 ± 0.5 km s−1 during the abovementioned intensity increase phase. It slowly reverted to 0 ± 0.5 km s−1 when the intensity decreased.
 IIA HARSH MATHUR
IIA HARSH MATHURClustering Analysis of Ca i 4227 Line Polarization Using Magnetohydrodynamic Simulations of the Solar Atmosphere
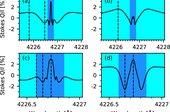
The Ca i 4227 Å line is a strong resonance line formed in the solar chromosphere. At the limb, it produces the largest scattering polarization signal. So far, modeling the linear polarization in this line has been limited to the use of one-dimensional semiempirical models of the solar atmosphere. Using three-dimensional magnetohydrodynamical models of the solar atmosphere, in this paper, we perform 1.5D radiative transfer calculations to understand the formation of linear polarization profiles due to resonance scattering in this line at a near limb position. We focus on studying the sensitivity of the resonance scattering polarization to the temperature and the density structures in the atmosphere. We do not include the effects of magnetic and velocity fields in this study. We use clustering analysis to identify linear polarization profiles with similar shapes and group them accordingly for our study. We analyze the structure of the linear polarization profiles across 14 clusters, each representing different realizations of the solar atmosphere. Using source function ratio plots at various wing and core wavelength positions, we provide a qualitative explanation of linear polarization profiles in these clusters.
 IIA JAYANT JOSHI
IIA JAYANT JOSHIOn the Million-degree Signature of Spicules
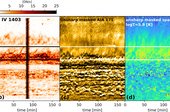
Spicules have often been proposed as substantial contributors toward the mass and energy balance of the solar corona. While their transition region (TR) counterpart has unequivocally been established over the past decade, the observations concerning the coronal contribution of spicules have often been contested. This is mainly attributed to the lack of adequate coordinated observations, their small spatial scales, highly dynamic nature, and complex multithermal evolution, which are often observed at the limit of our current observational facilities. Therefore, it remains unclear how much heating occurs in association with spicules to coronal temperatures. In this study, we use coordinated high-resolution observations of the solar chromosphere, TR, and corona of a quiet-Sun region and a coronal hole with the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph (IRIS) and the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) to investigate the (lower) coronal (∼1 MK) emission associated with spicules. We perform differential emission measure analysis on the AIA passbands using basis pursuit and a newly developed technique based on Tikhonov regularization to probe the thermal structure of the spicular environment at coronal temperatures. We find that the emission measure (EM) maps at 1 MK reveal the presence of ubiquitous, small-scale jets with a clear spatiotemporal coherence with the spicules observed in the IRIS/TR passband. Detailed spacetime analysis of the chromospheric, TR, and EM maps show unambiguous evidence of rapidly outward-propagating spicules with strong emission (2–3 times higher than the background) at 1 MK. Our findings are consistent with previously reported MHD simulations that show heating to coronal temperatures associated with spicules.
 IIA RENU DEVI
IIA RENU DEVIInvestigating the role of bars in quenching star formation using spatially resolved ultraviolet-optical colour maps
Bars are ubiquitously found in disc galaxies and they are known to drive galaxy evolution through secular processes. However, the specific contribution of the bars in the suppression of star formation is still a matter of debate.
Aims. Our aim is to investigate the role of bars in quenching star formation using spatially resolved UV-optical colour maps and radial colour profiles of a sample of 17 centrally quenched barred galaxies in the redshift range of 0.02–0.06.
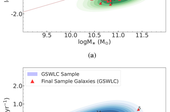
Methods. We selected the sample of centrally quenched barred galaxies based on their location in the SFR-M⋆ plane. They are classified as passive based on the parameters from the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics (MPA) and Johns Hopkins University (JHU) value-added catalogue (MPA – JHU VAC); however, they have also been classified as non-passive based on the parameters from the GALEX-SDSS-WISE Legacy (GSWLC) catalogue, indicating a passive inner region and recent star formation in their extended disc. We used the archival SDSS optical r-band and GALEX far- and near- ultraviolet (FUV and NUV) imaging data of these galaxies and created spatially resolved (FUV−NUV versus NUV−r) colour-colour maps to understand the nature of the UV emission from different regions of these galaxies. We also analysed their NUV−r colour radial profiles and use the NUV−r colour as a proxy for the stellar population age in the different regions of these galaxies. We also analysed a control sample of eight centrally quenched unbarred galaxies to disentangle the effect of bulge and bar in quenching star formation.
Results. The centrally quenched barred galaxies display redder colours (NUV−r > 4 – 4.5 mag) in the inner regions, up to the length of the bar, indicating the age of the stellar population in these regions is older than > 1 Gyr. Most barred galaxies in our sample host pseudo-bulges and do not host an active galactic nucleus (AGN), indicating that the most probable reason for the internal quenching of these galaxies is the action of stellar bar. In comparison to their unbarred counterparts, lying in a similar regime of stellar mass and redshifts, the barred galaxies show redder colours (NUV−r > 4 mag) to a larger spatial extent.
Conclusions. In their later stages of evolution, bars turn the inner regions of galaxies redder, leading to quenching, with the effect being most prominent up to the ends of the bar and creating a region dominated by older stellar population. This may occur because bars have already funneled gas to the galactic centre leaving behind no fuel for further star formation. Spatially resolved studies of a larger sample of barred galaxies at different redshifts will provide more insights to the role of bar in quenching star formation and the different evolutionary stages of quenching.
 IIA ANNAPURNI SUBRAMANIAM
IIA ANNAPURNI SUBRAMANIAMA Virgo Environmental Survey Tracing Ionised Gas Emission (VESTIGE) XVIII. Reconstructing the star formation history of early-type galaxies through the combination of their UV and Hα emission
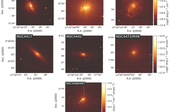
We reconstructed the star formation histories of seven massive (M⋆ ≳ 1010 M⊙) early-type galaxies (ETGs) in the Virgo cluster by analysing their spatially resolved stellar population (SP) properties including their ultraviolet (UV) and Hα emission. As part of the Virgo Environmental Survey Tracing Ionised Gas Emission (VESTIGE), we used Hα images to select ETGs that show no signs of ongoing star formation. We combined VESTIGE with images from Astrosat/UVIT, GALEX, and CFHT/MegaCam from the Next Generation Virgo Cluster Survey (NGVS) to analyse radial spectral energy distributions (SEDs) from the far-UV (FUV) to the near-infrared. The UV emission in these galaxies is likely due to old, low-mass stars in post main sequence (MS) phases, the so-called UV upturn. We fitted the radial SEDs with novel SP models that include an old, hot stellar component of post-MS stars with various temperatures and energetics (fuels). This way, we explored the main stellar parameters responsible for UV upturn stars regardless of their evolutionary path. We make these models publicly available through the SED fitting code CIGALE. Standard models are not able to reproduce the galaxies’ central FUV emission (SMA/Reff ≲ 1), while the new models well characterise it through post-MS stars with temperatures T ≳ 25 000 K. All galaxies are old (mass-weighted ages ≳10 Gyr) and the most massive ones, M49 and M87, are supersolar (Z ≃ 2 Z⊙) within their inner regions (SMA/Reff ≲ 0.2). Overall, we find flat age gradients (∇Log(Age) ∼ −0.04 − 0 dex) and shallow metallicity gradients (∇Log(Z) < −0.2 dex), except for M87 (∇Log(ZM87) ≃ −0.45 dex). Our results show that these ETGs formed with timescales τ ≲ 1500 Myr, having assembled between ∼40 − 90% of their stellar mass at z ∼ 5. This is consistent with recent JWST observations of quiescent massive galaxies at high-z, which are likely the ancestors of the largest ETGs in the nearby Universe. The derived flat and shallow stellar gradients indicate that major mergers might have contributed to the formation and evolution of these galaxies.
 IIA RAJAGURU, S. P
IIA RAJAGURU, S. PWave analysis tools
This Primer provides an overview of a fundamental set of analysis methods for studying waves, vibrations and related oscillatory phenomena — including instabilities, turbulence and shocks — across diverse scientific fields. These phenomena are ubiquitous, from astrophysics to complex systems in terrestrial environments, and understanding them requires careful selection of techniques. Misapplication of analysis tools can introduce misleading results. In this Primer, the fundamental principles of various wave analysis methods are first reviewed, along with adaptations to address complexities such as nonlinear, non-stationary and transient signal behaviour. These techniques are applied to identical synthetic datasets to provide a quantitative comparison of their strengths and limitations. Details are provided to help select the most appropriate analysis tools based on specific data characteristics and scientific goals, promoting reliable interpretations and ensuring reproducibility. Additionally, the Primer highlights best ethical practices for data deposition and the importance of open-code sharing. Finally, the broad applications of these techniques are explored in various research fields, current challenges in wave analysis are discussed, and an outlook on future directions is provided, with an emphasis on potential transformative discoveries that could be made by optimizing and developing cutting-edge analysis methods.
 IIA PRAMOD KUMAR, S
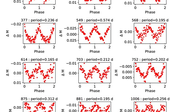
IIA PRAMOD KUMAR, SInvestigating pulsating variables and eclipsing binaries in NGC 2126 using ground- and space-based photometry, astrometry, spectroscopy, and modelling
Pulsating variables are prevalent in the classical Scuti instability strip of intermediate-age open star clusters. The cluster membership of these stars facilitates a comparative analysis of their evolution in analogous environments. In this study, we integrate ground-based observations, Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) Full Frame Images (FFIs), and Gaia Data Release 3 (DR3) data to investigate variable stars in the intermediate-age open star cluster NGC 2126. We performed ground-based time-series observations of NGC 2126 to identify variable stars within its vicinity. Next, we determined the membership of these stars using parallax and the proper motions from Gaia DR3 archive. Then, we searched the TESS FFIs for counterparts to the variables identified above and performed their frequency analysis and classification. Finally, we modelled the light curves (LCs) of detected eclipsing binaries (EBs), including V551 Aur, which has a pulsating component. We found 25 members and 85 field variable stars. In TESS FFIs, we found LCs for 11 known variables and a new rotational variable. We determined that the pulsating EB V551 Aur is a member of the cluster. The low- and medium-resolution spectra revealed the line profile variation and the basic parameters for the star, respectively. Simultaneous modelling of the eclipses and the embedded pulsations resulted in improved orbital parameters for the binary system. We also report the determination of orbital parameters for the previously uncharacterized EB system UCAC4 700−043174.
 IIA DIPANKAR BANERJEE
IIA DIPANKAR BANERJEECa ii K Polar Network Index of the Sun: A Proxy for Historical Polar Magnetic Field
The Sun's polar magnetic field is pivotal in understanding solar dynamo processes and forecasting future solar cycles. However, direct measurements of the polar field have only been available since the 1970s. The chromospheric Ca ii K polar network index (PNI; the fractional area of the chromospheric network regions above a certain latitude) has recently emerged as a reliable proxy for polar magnetic fields. In this study, we derive PNI estimates from newly calibrated, rotation-corrected Ca ii K observations from the Kodaikanal Solar Observatory (1904–2007) and modern data from the Rome Precision Solar Photometric Telescope (2000–2022). We use both of those Ca ii K archives to identify polar network regions with an automatic adaptive threshold segmentation technique and calculate the PNI. The PNI obtained from both the archives shows a significant correlation with the measured polar field from the Wilcox Solar Observatory (Pearson correlation coefficient r > 0.93) and the derived polar field based on an Advective Flux Transport Model (r > 0.91). The PNI series also shows a significant correlation with faculae counts derived from Mount Wilson Observatory observations (r > 0.87) for both Kodaikanal Solar Observatory and Rome Precision Solar Photometric Telescope data. Finally, we use the PNI series from both archives to reconstruct the polar magnetic field over a 119 yr long period, which includes the last 11 solar cycles (Cycles 14–24). We also obtain a relationship between the amplitude of solar cycles (in 13 month smoothed sunspot number) and the strength of the reconstructed polar field at the preceding solar cycle minimum to validate the prediction of the ongoing solar cycle, Cycle 25.